MicroRNA and Gene Regulation: Explained in Simple Terms
Gene regulation by microRNA can be understood in simple points:
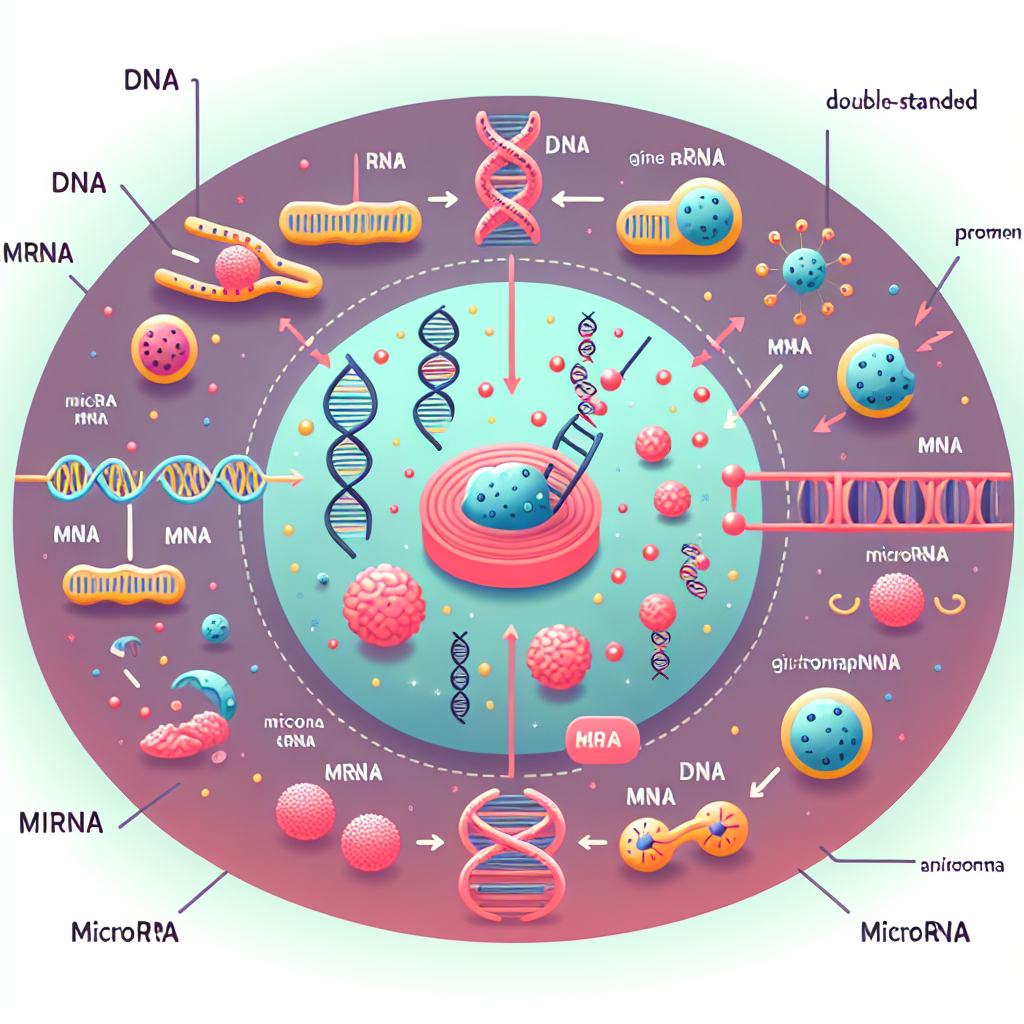
1. Genes are pieces of DNA that tell cells how to make proteins, which are essential for various functions in the body.
2. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are tiny molecules that play a role in controlling gene activity.
3. Each microRNA can bind to a specific messenger RNA (mRNA), which is the molecule that carries the instructions from DNA for making proteins.
4. When a microRNA binds to an mRNA, it can block the mRNA from being used to make a protein.
5. This means that the gene controlled by that mRNA is effectively turned down or silenced.
6. MicroRNAs help fine-tune the expression of genes, ensuring that proteins are made at the right time and in the right amount.
7. They are important in various biological processes, including development, cell growth, and response to stress.
8. Abnormal levels of microRNAs can be linked to diseases, including cancer, making them potential targets for new therapies.
In summary, microRNAs act like switches that can turn down the activity of certain genes, helping keep the balance in how proteins are produced in our cells.



Post Comment