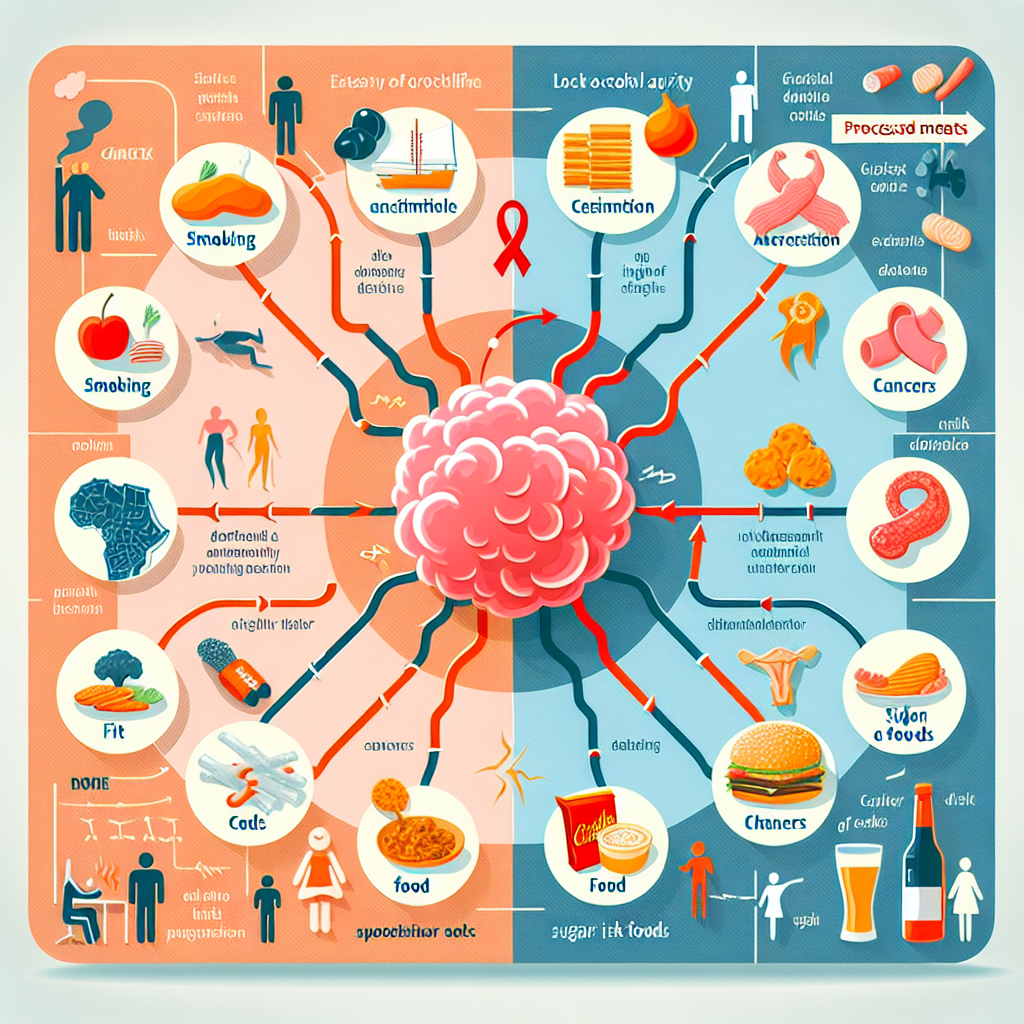
Everyday Habits and Foods That Increase Cancer Risk
1. Smoking
Smoking is one of the primary causes of cancer worldwide. According to the World Health Organization, tobacco use is responsible for more than 8 million deaths each year. Cigarette smoke contains over 7,000 chemicals, many of which are known carcinogens. For instance, benzene and formaldehyde are potent cancer-causing agents found in tobacco. Even secondhand smoke poses a significant risk, contributing to approximately 1.2 million premature deaths. The connection between smoking and lung cancer is well-established, but it also increases the risk of various other cancers, including bladder, mouth, and throat cancers.
2. Alcohol Consumption
Excessive alcohol consumption is another significant risk factor for cancer. The American Cancer Society states that alcohol consumption is linked to at least seven different types of cancer, including breast, liver, and colorectal cancers. Studies indicate that individuals who regularly consume more than two alcoholic drinks per day have a higher risk of these cancers. In fact, one study estimated that nearly 5.8% of all cancer cases in the U.S. are attributable to alcohol. The carcinogenic effects of alcohol are thought to stem from its metabolization into acetaldehyde, a substance that can damage DNA.
3. Obesity
Obesity is a growing epidemic worldwide, and it is directly linked to an increased risk of several types of cancer. The World Health Organization reports that overweight and obesity accounted for approximately 2.8 million deaths each year. Studies have shown that being overweight can affect hormone levels in the body, leading to conditions that may increase cancer risk, such as insulin resistance and inflammation. In fact, the American Institute for Cancer Research states that about 14% of all cancer cases in the U.S. are related to obesity, particularly breast, colon, and endometrial cancers.
4. Processed Meats
Consumption of processed meats has been classified by the International Agency for Research on Cancer as a Group 1 carcinogen, meaning there is sufficient evidence that it causes cancer in humans. Studies have found that eating just 50 grams of processed meat daily can increase the risk of colorectal cancer by 18%. Examples of processed meats include bacon, sausages, and deli meats. The carcinogenicity of these foods is thought to stem from the nitrates and nitrites used in preservation, which can form cancer-causing compounds during cooking.
5. Red Meat
Red meat is another food item that has been linked to an increased cancer risk. While it does not carry the same classification as processed meats, many health organizations recommend limiting red meat intake. Research suggests that high consumption of red meat, particularly when cooked at high temperatures (like grilling or barbecuing), may elevate the risk of developing colorectal cancer. The World Health Organization suggests limiting red meat intake to approximately 500 grams per week to minimize cancer risk.
6. Sugar and High-Glycemic Foods
Diets high in sugar and refined carbohydrates can promote obesity and insulin resistance, both of which are risk factors for cancer. Foods with a high glycemic index can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar, leading to an increase in insulin production and possibly fostering an environment conducive to cancer cell growth. A study published in the journal Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers, & Prevention found that high sugar intake was associated with a greater risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. Reducing sugar and processed carbohydrate consumption can help mitigate cancer risk and support overall health.
7. Lack of Physical Activity
Physical inactivity can contribute significantly to obesity and metabolic issues, which in turn heighten cancer risk. The American Cancer Society indicates that a lack of regular physical activity is associated with an increased risk of several types of cancer, including breast, prostate, and colon cancers. Regular exercise helps regulate body weight, improves insulin sensitivity, and decreases inflammation, all of which are important in reducing cancer risk. Aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week can improve overall health and reduce cancer risk effectively.
8. Exposure to Environmental Pollutants
Environmental pollutants can also raise cancer risk significantly. Soil, air, and water can contain numerous carcinogenic substances, such as benzene, formaldehyde, and certain heavy metals. Studies have demonstrated that long-term exposure to pollution can increase the likelihood of various cancers, including lung and bladder cancer. The American Cancer Society has indicated that the urban air quality management plays a crucial role in cancer prevention. Advocating for cleaner air and supporting policies aiming at reducing emissions can ultimately lead to reduced cancer rates.
9. High Salt Intake
Diets high in salt can also be of concern regarding cancer risk. Excessive salt intake may lead to stomach cancer, particularly in individuals consuming a diet deficient in fresh fruits and vegetables. The International Agency for Research on Cancer has classified pickled vegetables and salted fish as Group 1 carcinogens. It is advisable to limit sodium intake to less than 2,300 milligrams per day to minimize health risks, including stomach cancer.
10. Poor Dietary Choices
In addition to specific foods, overall poor dietary choices can increase cancer risk. Diets that lack adequate fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fiber can lead to health issues that contribute to cancer risk. The American Institute for Cancer Research recommends focusing on plant-based foods, as they contain essential nutrients, antioxidants, and phytochemicals that have protective effects against cancer. A diet rich in diverse, colorful fruits and vegetables can lower cancer risk and promote long-term health.
In conclusion, understanding the habits and foods that pose a risk for cancer is essential in making informed choices for a healthier lifestyle. By addressing issues like smoking, alcohol consumption, and dietary habits, individuals can significantly reduce their cancer risk and improve overall well-being. Making simple lifestyle changes can have far-reaching effects on health and longevity.


Post Comment